Graph Representation
Author: Muhammad Hasan (IF 2018)
Graph is an abstract data type, structured with vertex/node and edge. Here is a simple example:
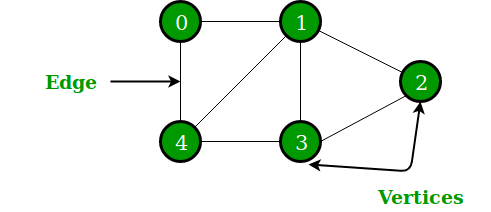
Graph could be represented in many ways in programming, here are some of the most common ways.
Adjacency Matrix
The adjacency matrix, sometimes also called the connection matrix, of a simple labeled graph is a matrix with rows and columns labeled by graph vertices, with a or in position according to whether and are adjacent or not. If the graph has a weight, than you can simply change in the matrix with it's weight, and if for some and there isn't any edge, you can store it as or .

In C++, we can use array, or a vector to store this:
int n; // number of nodes cin >> n; vector<vector<int>> matrix(n, vector<int>(n)); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { int value; cin >> value; matrix[i][j] = value; } }
This represantion obviously takes memory, where is the number of node, and because of that, this isn't good representation, but it's useful for small graphs.
Edge List
An edge list is a data structure used to represent a graph as a list of its edges. An (unweighted) edge is defined by its start and end vertex, so each edge may be represented by two numbers.

In C++, we can store this simply with a list of pair:
int m; // number of edges cin >> m; vector<pair<int, int>> edges; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int u, v; cin >> u >> v; edges.push_back(make_pair(u, v)); }
This representation takes memory, where is the number of edge. This representation is usually used for finding Minimum Spanning Tree.
Adjacency List
In graph theory and computer science, an adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a vertex in the graph. This is one of several commonly used representations of graphs for use in computer programs.

This graph representation is often used in CP, mainly because it's easy to do traversal in the graph with this representation.
In C++ you can store it with an array of vectors:
const int N = number_of_nodes; vector<int> adj[N]; int m; // number of edges cin >> m; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int u, v; cin >> u >> v; adj[u].push_back(v); adj[v].push_back(u); // remove this if it's directed }
This representation takes memory.
Depth First Search
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.

We can implement this in C++ with an adjacency list, array of visited nodes, and a dfs method (or a stack data structure):
bool vis[N]; // set automatically to false if declared globally void dfs(int u) { vis[u] = 1; // marks as visited for (auto v : adj[u]) { if (vis[v]) continue; // if already visited, continue dfs(v); // do dfs on the node v } }
Breadth First Search
Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. It starts at the tree root (or some arbitrary node of a graph, sometimes referred to as a 'search key'), and explores all of the neighbor nodes at the present depth prior to moving on to the nodes at the next depth level.
It uses the opposite strategy as depth-first search, which instead explores the node branch as far as possible before being forced to backtrack and expand other nodes.
To implement it in C++, it's quite similar to DFS, but instead of using a stack, we use the queue data structure:
bool vis[N]; int source; // The source/first node to be pushed queue<int> q; vis[source] = 1; // marks as visited q.push(source); // push the source node to the queue while (!q.empty()) { int u = q.front(); // takes the front element of the queue q.pop(); // pops the front element for (auto v : adj[u]) { if (!vis[v]) { // if not yet visited vis[v] = 1; // mark as visited q.push(v); // push to the queue } } }
Shortest Path
In graph theory, the shortest path problem is the problem of finding a path between two vertices (or nodes) in a graph such that the sum of the weights of its constituent edges is minimized.
We will see three common ways to find shortest path in graph.
Floyd Warshall
In computer science, the Floyd–Warshall algorithm (also known as Floyd's algorithm, the Roy–Warshall algorithm, the Roy–Floyd algorithm, or the WFI algorithm) is an algorithm for finding shortest paths in a weighted graph with positive or negative edge weights (but with no negative cycles).
To implement this, we need to use Adjacency Matrix, here is the implementation in C++:
const int INF = INT_MAX; // Infinite Value int n; // number of nodes cin >> n; vector<vector<int>> dist(n, vector<int>(n, INF)); // sets all the distance to INF for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) // for every (i, i) set its distance to 0 dist[i][i] = 0; int m; // number of edges cin >> m; // Take input edges and update distances for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int u, v, w; // edge from u to v with weight equals to w cin >> u >> v >> w; dist[u][v] = w; dist[v][u] = w; // remove this if it's directed } // Use Floyd Warshall to find every shortest path pair for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j], dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]); } } } // we will have dist[i][j] -> shortest path value from node i to node j
This algorithm has a time complexity of , where is the number of nodes. And so it can only be used for small graphs.
Bellman Ford
The Bellman–Ford algorithm is an algorithm that computes shortest paths from a single source vertex to all of the other vertices in a weighted digraph. It's useful to handle negative cycle. You can read more detailed description here.
Dijkstra
Dijkstra's algorithm (or Dijkstra's Shortest Path First algorithm, SPF algorithm) is an algorithm for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a graph, which may represent, for example, road networks. You can read more detailed description here.